Experiment No.: 1
Experiment Name:
Dismantle MCCB/ELCB/ RCCB and Identification of Various Parts
Objectives:
- To dismantle MCCB, ELCB, RCCB
- To identify different parts
Theory:
1. MCCB: Molded Case Circuit Breaker or MCCB is an automatic electrical device. It is a type of circuit breaker that protects the circuit from overloading, short circuit and current surges. It is an advanced version of miniature circuit breaker MCB since it operates like one. However, it offers extra features that make it a superior circuit breaker such as remote closing and adjustable trip settings i.e. its current settings and time settings can be adjusted according to our needs.
Basic circuit diagram of MCCB:
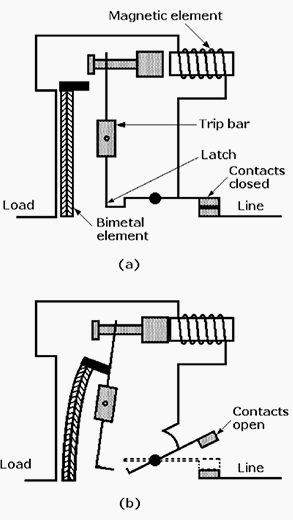
Parts of an MCCB:
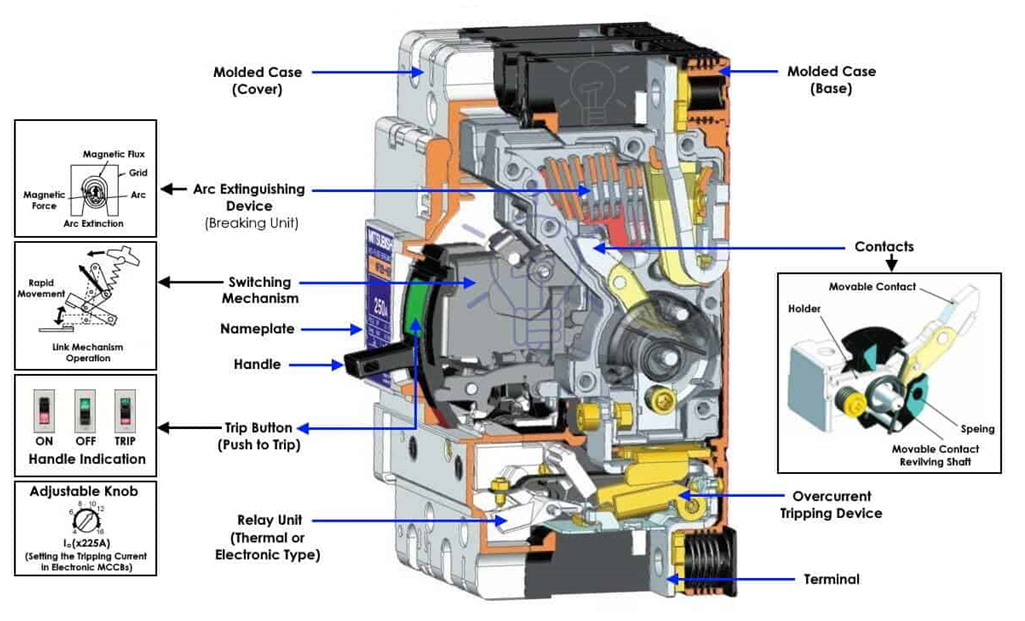
2. ELCB: An Earth-leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical installations with high Earth impedance to prevent shock. It detects small stray voltages on the metal enclosures of electrical equipment, and interrupts the circuit if a dangerous voltage is detected. Once widely used, more recent installations instead use residual current circuit breakers which instead detect leakage current directly.
The main purpose of Earth leakage protectors is to prevent injury to humans and animals due to electric shock. This is a category of devices, which are used to protect instruments, circuits and operators, while Earth leakage. Early ELCBs were voltage operated devices (VO-ELCB), detecting a voltage rise between installation metalwork, and an external electrode. These have now been replaced by current sensing devices (RCD/RCCB). In modern literature voltage sensing devices are called ELCB or VOELCB and current sensing devices are called RCCB or RCD. There are two types of earth leakage circuit breaker, one is voltage ELCB and other is current ELCB.
Basic Circuit Diagram of an ELCB:
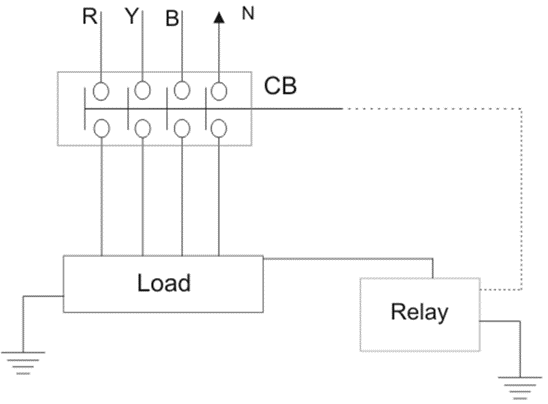
Parts of an ELCB:
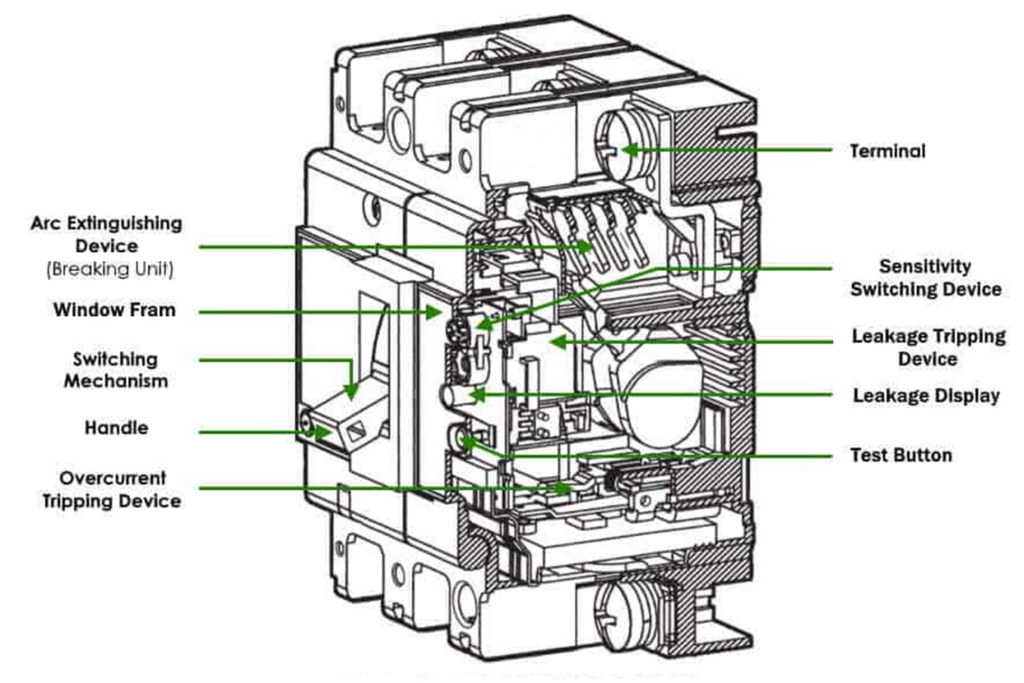
3. RCCB: The working principle of current earth leakage circuit breaker or RCCB is also very simple as voltage operated ELCB but the theory is entirely different and residual current circuit breaker is more sensitive than ELCB. Here one CT (Current Transformer) core is energized from both phase wise and neutral wire.
The polarity of the phase winding and neutral winding on the core is so chosen that, in normal condition mmf of one winding opposes that of another. As it is assumed that, in normal operating conditions the current goes through the phase wire will be returned via neutral wire if there’s no leakage in between. As both currents are same, the resultant mmf produced by these two currents is also zero-ideally.
The relay coil is connected with another third winding wound on the CT core as secondary. The terminals of this winding are connected to a relay system. In normal operating condition there would not be any current circulating in the third winding as here is no flux in the core due to equal phase and neutral current. When any earth leakage occurs in the equipment, there may be part of phase current passes to the earth, through the leakage path instead of returning via mental wire. Hence the magnitude of the neutral current passing through the RCCB is not equal to phase current passing through it.
Basic Circuit Diagram of RCCB:
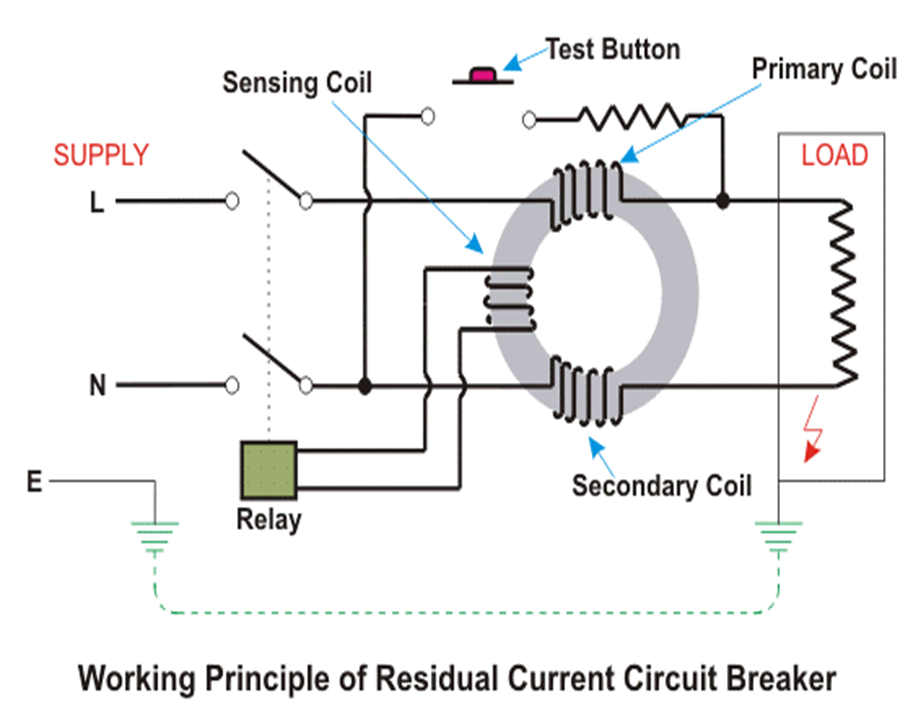
Parts of RCCB:
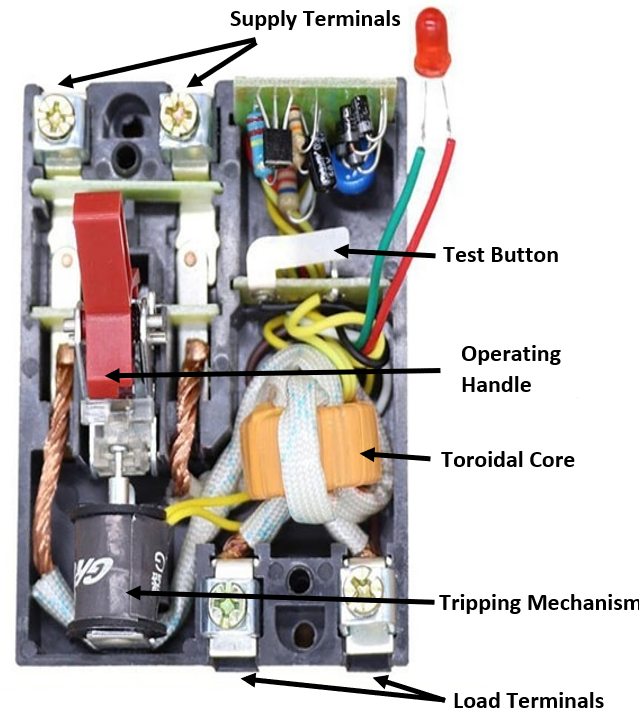
Apparatus Used:
| Sl No. | Name of Apparatus | Specification | Quantity | Makers name |
| 1. | MCCB | 1 | ||
| 2. | ELCB | 40A, 2P, I∆n- 100 mA, Un- 240/415V, Ut- 240V, 50 Hz, Im- 3000A, Inc- 10000A | 1 | JUVAS |
| 3. | RCCB | In- 63A, Un- 240V, I∆n- 30mA | 1 | ABB |
Remarks: MCCB, RCCB and ELCB are dismantled and different parts are identified.
