Experiment No.: 1
Experiment Name:
Measurement of strain by using a basic strain gauge and hence determine the stress induced.
Objective:
- To measure strain by using a basic strain gauge
- To determine the stress induced
Theory:
It is a resistive transducer as well as passive transducer and it works on the basis of familier equation of resistance, R= ρ. l/a.
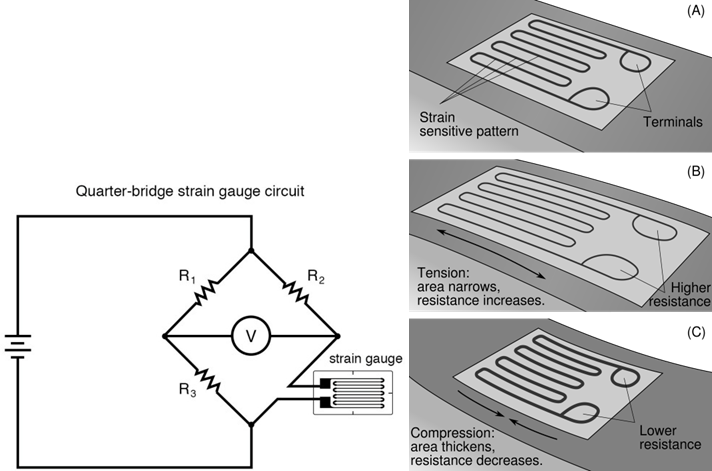
The non electric quantity (Displacement, force, pressure, temperature etc) which has to be measured is applied on such a way that these will change either length or cross sectional area of resistive wire. Resistive wire strain gauges also known as “Piezo-resistive Gauge”. It is used for measurement of displacement, temperature and pressure. As a secondary transducer it also used for measurement of force and acceleration.
Circuit Diagram:
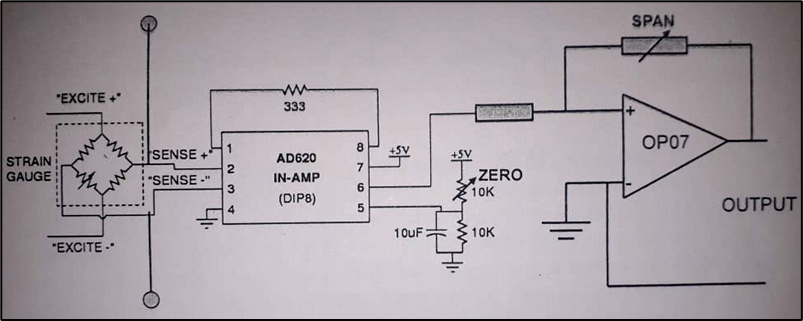
Observation Table:
| Sl. No. | Applied mass (gm) | Displayed mass (gm) | % Error | Change in voltage (Δeo) (mV) | Input Voltage (ei) (V) |
Graph:
From the observation table a graph is plotted. Mass v/s change in voltage (Δeo)
Determination of Stress:
Stress= Force/area, Force= mass. gravitational acceleration,
So, calculated stress= m.g/a where, m= applied mass, g= gravitational acceleration, a= elevated surface area of strain gauge.
Taken, g= 9.81 m/s2 and a= _______ m2
| Sl. No. | Mass (gm) | Stress (N/m) |
| 1. | ||
| 2. | ||
| 3. | ||
| 4. |
Apparatus Used:
| Sl No. | Name of Apparatus | Quantity | Specification | Makers name |
| 1. | Strain measurement trainer kit | 1 | Resistive type strain gauge | M.E.W. |
| 2. | Weight Box | 1 | 500 gm | |
| 3. | Digital Multimeter | 1 | 0-750 V AC, 0-10 A | Akademika |
Remarks:
Views: 25
