Experiment No.: 7
Experiment Name:
Study of different lightning arrester and identify different parts.
Objective:
- To study of different lightning arrester
- To identify different parts of it
Theory:
A lightning arrester is a device used on electric power transmission and telecommunication systems to protect the insulation and conductors of the system from the damaging effects of lightning. The typical lightning arrester has a high-voltage terminal and a ground terminal. When a lightning surge (or switching surge, which is very similar) travels along the power line to the arrester, the current from the surge is diverted through the arrester, in most cases to earth.
There are different types of LA used in electrical power system, are discussed below:
- Rod gap arrester
- Sphere gap arrester
- Horn gap arrester
- Multigap arrester
- Metal oxide arrester
- Rod Gap Arrester: It is one of the simplest types of Lightning Arresters. There is a gap between the end of the two rods. These two rods get connected to the earth and the line directly. The gap gets filled with air. When there is a higher voltage on the line, the air ionizes, producing a spark. In this fashion, the fault current passes to the earth. The process is explicated above in the snippet. Hence, the equipment is saved from potential damage.


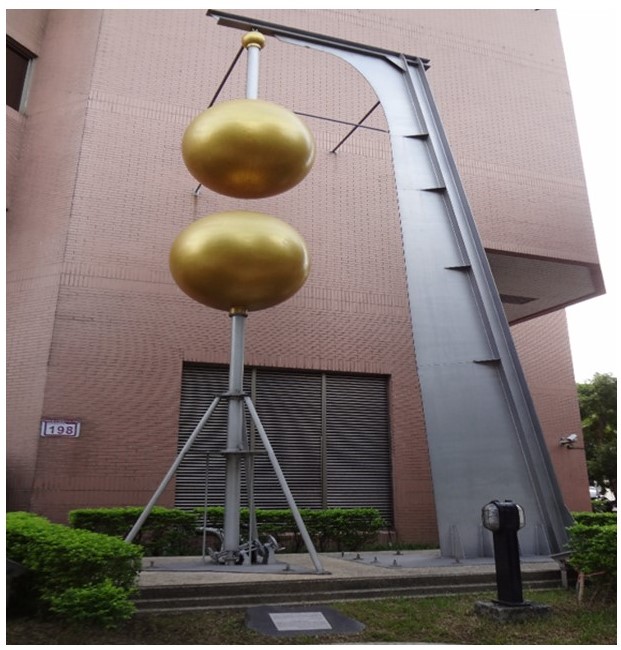
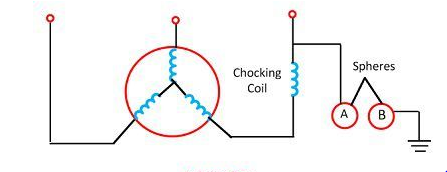
2. Sphere Gap Arrester: In such types of lightning arresters, an air gap is provided between two spheres. Here, one of the spheres is grounded, and another is connected to the line. The diagram below represents the process in detail. There is a choking coil between the transformer and the ground, which heats up when the voltage rises. The air between the spheres heats up and tries to escape. But the corona discharge mechanism ionizes the air and the fault current passes through it. Thus, it saves potential damage to the device.

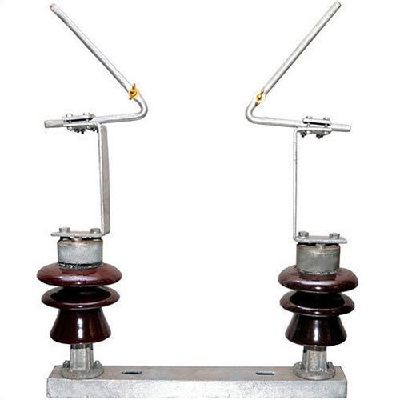
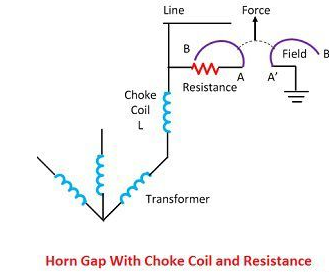
3. Horn Gap Arrester: This contains two horn-shaded pieces of metal. These two are separated by a small air gap and connected in a shunt between each conductor and earth. The distance between the two electrodes is optimum. This distance is filled with air that ionizes on fault current passage. Hence, the fault current is passed to the earth, and the inherent damage is stopped.

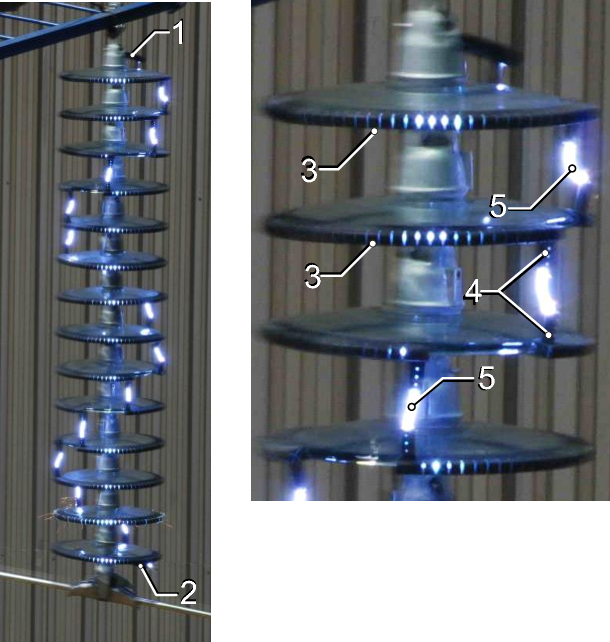
4. Multigap Arrester: The schematic diagram above shows the details in brief. It consists of a small series of insulated through an air gap. The number of gaps depends upon the voltage. The gaps protect the device through the corona discharge. In it, air ionizes, and fault current passes through the ground. A resistor is added to stop the fault current even further.

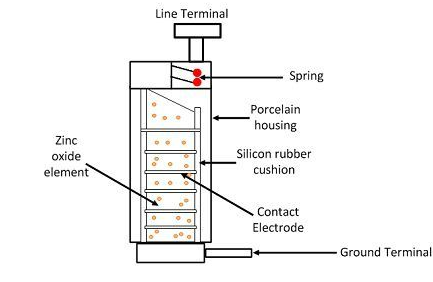
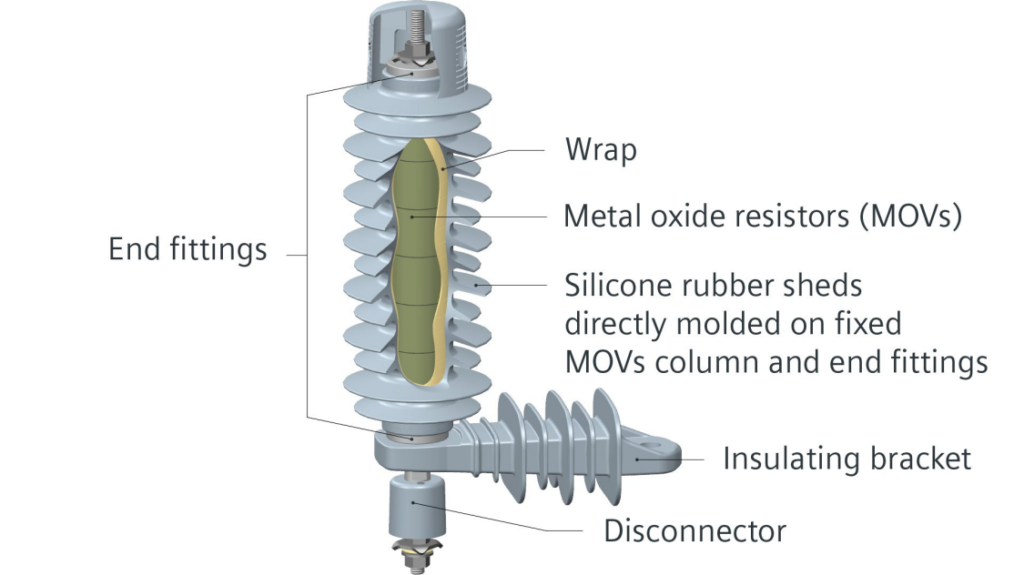
5. Metal Oxide LA: These types of diverters are known as gapless surge diverters. The base material here is zinc, and the oxide manufactured is zinc oxide. It is a semiconducting material. This material is anesthetized by adding fine powders of insulating oxides.
This powder is treated and then stuffed into a disc-shaped structure. The disc is then enclosed in an earthenware housing filled with sulfur hexafluoride.
Thus, the arrester consists of a potential obstacle at the edges of zinc oxide. This potential barrier constrains the river and pathways of the current. Under normal conditions, it stops the flow of current. But when there is a potential breakage, the barrier collapses and the fault current passes to the ground.
Thus, this stops the surge from damaging any device.
Remarks:
The different types and parts of lightning arrester are studied properly.
