Experiment No.: 4
Experiment Name:
Identify the Routine Maintenance Parts of the Large Hydro Power Plant after Watching a Video Programme
Objective:
To identify different parts of large hydro power plant.
Theory:
The major components of a Hydroelectric Power Plant are:-
- Dam/Barrage- Head works i.e. power intake, head regulator and desilting chambers etc.
- Head race tunnels/channels
- Surge tank
- Pressure shaft/Penstock
- Sluice Valve
- Underground and surface power house
- Turbine
- Tailrace channel or tailrace tunnel
Schematic Diagram:
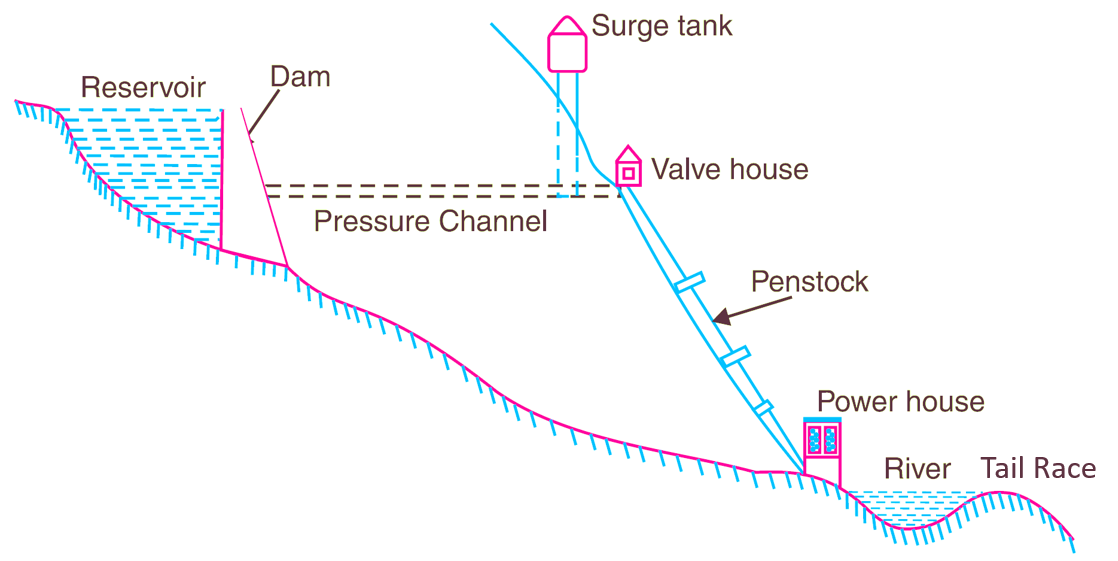
- Dam/Barrage: Dams are just one component of a complete hydroelectric facility, but are one major, visible component in the system. The purpose of a hydroelectric dam is to provide a place to convert the potential and kinetic energy of water to electrical energy by using a turbine and generator. Dams act as the place where water is held back and released in a controlled manner through hydraulic turbines, enabling the mechanical energy of the water to be transformed to electrical energy.
- Head Race Tunnel: The headrace conduit, conveys the water from the reservoir to the turbine. The conduit can be a channel, flume, penstock, tunnel, or combinations of these. The length of the headrace can vary from a few meters to several kilometers.
- Surge Tank: Surge tanks are applied in hydropower plants with long water conduits to reduce pressure forces during the acceleration of the large water masses. They are constructed as intermittent water reservoirs close to the turbines, either with open access to atmospheric air or as a closed volume filled with pressurized air. The surge tanks reduce the length of the water column to be accelerated, and thus the resulting pressure forces. This reduction is necessary to limit the design pressure for structural components and to enable “speed governing” of the turbines.
- Penstock: Penstocks are pipes or long channels that carry water down from the hydroelectric reservoir to the turbines inside the actual power station. Generally, they are made of steel and water under high pressure flows through the penstock. They are a vital component of a hydroelectric facility that allows water to move to the turbine. Grates or filters can be attached to the ends of penstocks to trap large debris such as branches. This ensures that debris cannot enter the channel and block it.
- Sluice Valve: The amount of water that is allowed to flow through the penstock can be controlled with a sluice, which is simply a gate that can be raised and lowered to increase or decrease the amount of water allowed to flow through. When the sluice is fully open, water flows freely down through the penstock. However, when it is closed slightly there is a limitation to how much water can flow, and thus less water enters the penstock.
- Power House: Power house is a building provided to protect the hydraulic and electrical equipment. Generally, the whole equipment is supported by the foundation or substructure laid for the power house.
- Turbine: Turbines convert the energy of rushing water, steam or wind into mechanical energy to drive a generator. The generator then converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. In hydroelectric facilities, this combination is called a generating unit. Some types of turbine used in hydel power plant, mentioned below,
- Kaplan turbine
- Fransis turbine
- Pelton wheel turbine
- Tailrace channel or tailrace tunnel: The tail race, containing tail water, is a channel that carries water away from a hydroelectric plant or water wheel. The water in this channel has already been used to rotate turbine blades or the water wheel itself. This water has served its purpose, and leaves the power generation unit or water wheel area.
Maintenance of hydel power plant:
Routine maintenance services normally take one day for two hydropower service technicians to complete and covers:
- Turbine functional checks and inspection.
- Turbine bearing lubrication and inspection.
- Gearbox inspection.
- Gearbox oil condition analysis and oil changes.
- Gearbox bearing inspection and lubrication.
- Drive belt inspection and replacement.
- Drive coupling inspection.
- Generator inspection.
- Generator bearing inspection and lubrication.
- Hydraulic system inspection.
- Hydraulic system oil condition analysis and oil changes.
- Check all sensors operate correctly.
- Check controller functions correctly.
- Inspection of intake area, impounding structures, pipeline, sluice(s).
Conclusion:
In this way we identify the routine maintenance parts of large hydro power plant.
Views: 364
