Experiment No.: 5
Experiment Name:
Study of Samples of Underground Cables
Objectives: To study
- PILC cable
- PVC cables
- XLPE cables
Theory:
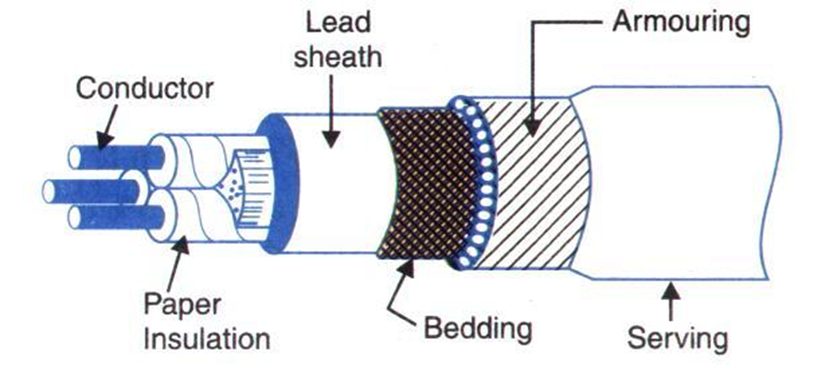
1.PILC (Paper Insulated Lead Covered) Cable: Paper insulated lead covered high voltage mains power cable
- Conductor: Plain annealed stranded compacted copper
- Core identification: Numbered cores
- Insulation: M.I.N.D (Mass impregnated non-draining) paper insulated, lead or lead alloy sheathed
- Screen: Belted or Screened
- Bedding: Textile compound
- Armour/Protection: SWA (Single wire armour)
- Sheath/Jacket: PVC (Polyvinyl chloride)
- Colour: Red
- Voltage: 6350/11000v
- Operating temperature: Maximum 80°C, minimum bending 0°C
- Standards: BS 6480 : Power cables, impregnated paper insulated, lead or lead alloy sheathed electric cables
- Applications: mains power distribution cable
Constructional figure of 3 core PILC Cable:
2. PVC (Poly Vinyl Chloride) Cable: As PVC (Poly Vinyl Chloride) is a thermoplastic polymer, PVC properties make it suitable for applications where the cables may be exposed to high or low temperatures (including use of arctic-grade PVC for extreme low conditions), or where protection against UV light is required to avoid degradation. PVC insulation is frequently used owing to its good insulating properties but low corona resistance, and is best suited for low and medium voltage cables and low frequency insulation requirements.
- Voltage: up to 6/10 kV
- Operating temperature: 70o, 85o and 105 oC.
- Applications: Mains electricity wiring, Flexible panel wire, General wiring in public areas, power, lighting and internal wiring cable. Also suitable for AC and DC telecommunications applications
- The benefits of PVC as cable insulation and sheathing material include its chemical stability, robustness and durability.
Constructional figure of 3&½ core PVC Cable:

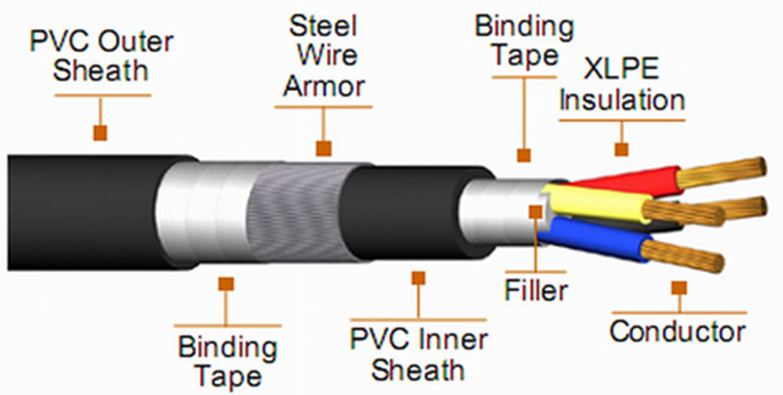
3. XLPE (Cross(X) Linked Polyethylene) Cable: XLPE or Cross-linked polyethylene is a thermoset insulation material. Physical cross-linking involves subjecting the polymer to a high energy source such as high-energy electron or microwave radiation.
Polyethylene (PE) material itself has excellent dielectric strength, high insulation resistance, and a low dissipation factor at all frequencies making it an ideal insulator; however it is limited in its temperature range. Cross-linking the PE to become XLPE increases the temperature range of the insulation whilst maintaining the electrical properties.
- Voltage: Medium Voltage XLPE Cables (11KV- 36KV)
- Operating temperature: XLPE Cables are manufactured as per IS:7098/ Part-II to be suitable for conductor temperature of 90°C and short circuit temperature 250°C.
- Application: in building services pipework systems, hydronic radiant heating and cooling systems, domestic water piping, and insulation for high tension (high voltage) electrical cables. It is also used for natural gas and offshore oil applications, chemical transportation, and transportation of sewage and slurries.
Constructional figure of 3&½ Core XLPE Cable:
Remarks: The different parts of the underground cables (XLPE, PVC, PILC) are identified successfully.
